Understanding the Greatest Influences on Young Children’s Lifestyles: Key Factors, Real-World Impact, and Practical Guidance
Introduction: Why Lifestyle Matters in Early Childhood
Early childhood is a critical period that lays the foundation for lifelong health, learning, and emotional well-being. Numerous studies confirm that the lifestyle of young children is shaped by a complex interplay of factors, including family, socioeconomic status, education, physical and emotional health, and environmental influences. Understanding these factors is essential for caregivers, educators, and community leaders who aim to foster positive outcomes for children and address barriers to healthy development [1] , [3] .
1. The Central Role of Family Environment
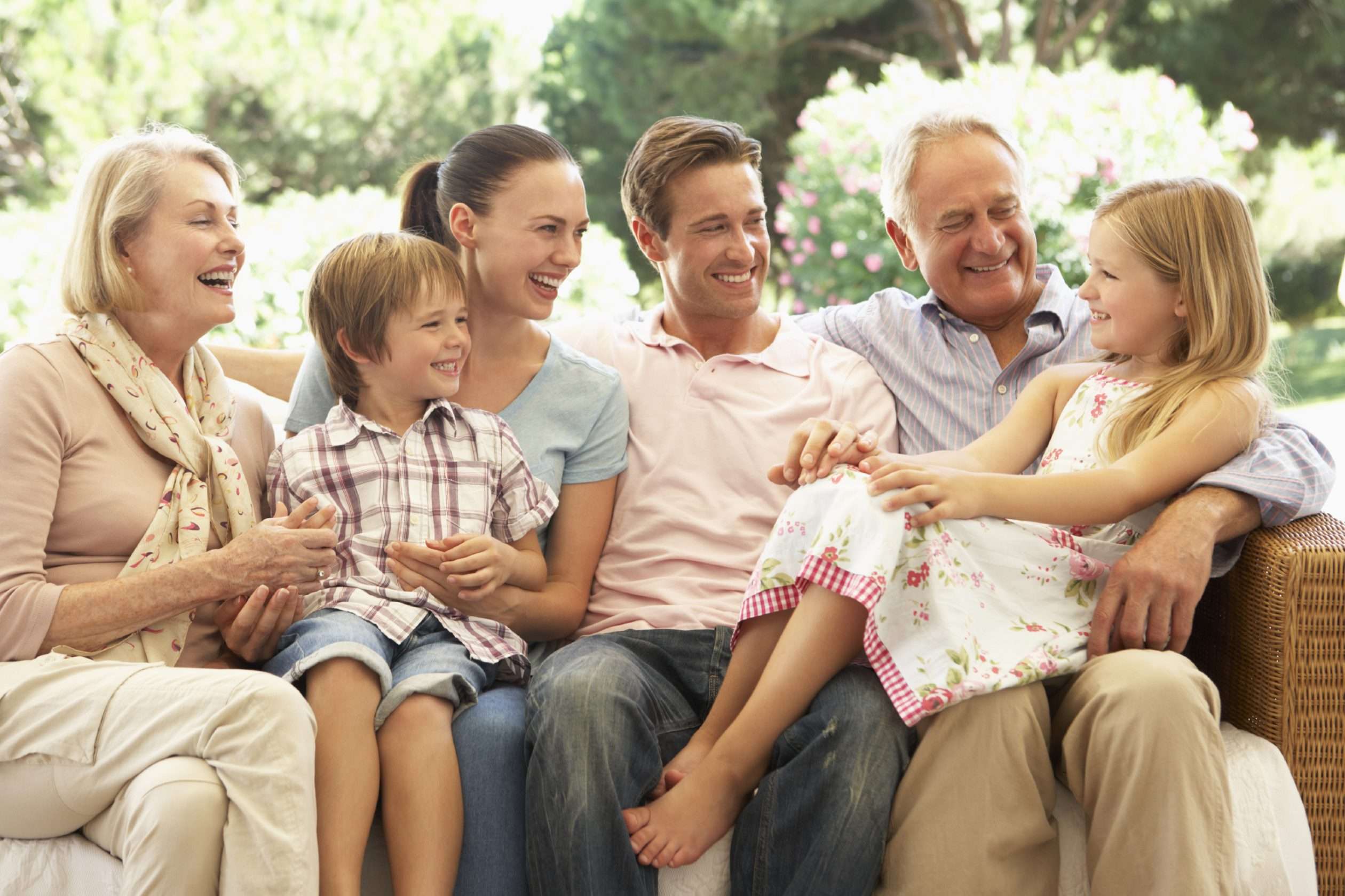
Family environment is consistently identified as the single most influential factor in shaping the lifestyle and development of young children. The emotional stability of the home, the presence of strong attachment bonds, and the quality of parental interactions directly affect social, emotional, and cognitive growth. Children who experience nurturing, safe, and supportive family environments are more likely to develop healthy emotional regulation, self-esteem, and resilience [2] .
For instance, children in homes where caregivers actively engage in stimulating activities-such as reading, playing, and conversing-demonstrate stronger language skills and improved school readiness. Conversely, families facing instability, high stress, or conflict may inadvertently create barriers to healthy development, often resulting in increased behavioral and emotional challenges [1] .

Source: ar.inspiredpencil.com
Actionable Guidance:
If you are a parent or caregiver, prioritize creating a stable and emotionally supportive environment. This can include establishing routines, expressing affection consistently, and providing enriching experiences. For those seeking help, consider contacting your local child and family services agency or searching for “parenting support programs” in your area for workshops and counseling.
2. Socioeconomic Status: The Foundation of Opportunity
Socioeconomic status (SES) profoundly impacts a child’s lifestyle, affecting access to nutritious food, safe housing, educational opportunities, and healthcare. Research indicates that children in higher-SES households are more likely to engage in physical activity, participate in organized sports, and access quality educational resources, all of which support physical and cognitive growth [4] .
Low-SES families may face challenges such as housing instability, food insecurity, and elevated stress, contributing to higher rates of developmental delays and mental health issues. For example, children raised in poverty are at increased risk for behavioral problems and academic underachievement [1] .
Actionable Guidance:
Families seeking financial assistance or community resources can search for “family support services” or contact local government offices for programs related to food security, housing assistance, and child healthcare. For educational support, inquire about early childhood programs and scholarships available through your school district or state education department.
3. Quality of Education and Early Learning Opportunities
Access to quality education and early learning experiences is a major determinant of children’s cognitive and social development. Early childhood education programs provide structured environments that encourage problem-solving, creativity, and social interaction. Children who attend high-quality preschools or kindergarten programs typically enter school better prepared cognitively and emotionally [3] .
Unfortunately, disparities in access to quality early education persist, particularly in underserved communities. Limited availability of stimulating activities and exposure to language-rich environments can hinder development, while supportive school settings with trained educators promote positive outcomes.
Actionable Guidance:
To locate early childhood programs, use search terms like “preschool enrollment,” “Head Start programs,” or “early childhood education” with your city or county. For additional support, contact your local school district’s early learning coordinator or visit the official education department website for program listings.
4. Physical Health: Nutrition, Sleep, and Activity
Physical health factors-including diet, sleep habits, and physical activity -have a direct and measurable impact on children’s lifestyle and well-being. Studies show that poor nutrition, lack of sleep, and sedentary behavior are linked to increased risk of obesity, cognitive delays, and behavioral issues [1] .
For example, children who regularly engage in physical activity and consume a balanced diet are more likely to maintain healthy weight, develop strong motor skills, and perform better academically. On the other hand, sleep deprivation and poor nutrition can negatively affect mood, attention span, and long-term health outcomes.
Actionable Guidance:
Parents can support healthy habits by establishing regular mealtimes, encouraging play and exercise, and maintaining consistent sleep routines. For assistance with nutrition, seek guidance from licensed pediatricians or registered dietitians. Many local health departments offer free or low-cost nutrition counseling; search for “child nutrition programs” in your region.
5. Environmental Influences: Safety, Pollution, and Social Context
Environmental factors -such as housing conditions, exposure to toxins, neighborhood safety, and cultural context-also shape children’s lifestyles in powerful ways. Exposure to environmental hazards like lead or air pollution can result in developmental delays and poor academic performance, disproportionately affecting children in low-income or minority communities [3] , [4] .
Children living in unsafe neighborhoods may experience chronic stress, limiting outdoor play and social interaction. Community organizations, local government agencies, and public health departments often provide resources to improve housing safety, reduce environmental risks, and foster healthy community environments.
Actionable Guidance:
If you suspect environmental risks in your home or neighborhood, contact your local public health department for free testing and remediation services. For guidance on safe housing, use search phrases like “child-safe housing resources” and reach out to community organizations specializing in family health and safety.
6. Emotional and Social Development: Peer Relationships and Behavioral Health
Children’s emotional development and ability to establish positive peer relationships are essential for a healthy lifestyle. Supportive interactions with peers and caregivers help children develop empathy, self-regulation, and social competence. Conversely, exposure to bullying, isolation, or adverse relationships can lead to behavioral problems, lower academic performance, and diminished self-worth [5] , [4] .
Interventions such as social skills groups, counseling, and school-based programs can support children struggling with emotional or behavioral challenges. Early identification and intervention are key to preventing long-term difficulties.
Actionable Guidance:
If you are concerned about your child’s emotional health or peer relationships, consult with a pediatrician, school counselor, or licensed child therapist. Many schools offer social-emotional learning programs and can connect families to community-based resources.

Source: philfilmrhodes.blogspot.com
Alternative Pathways and Additional Resources
While family and socioeconomic status remain the most impactful, every child is unique, and a combination of factors may shape their lifestyle. For families seeking additional support, consider:
- Contacting local family service agencies for comprehensive assessments and referrals
- Searching for “early childhood development programs” and “community support for families” in your area
- Consulting with healthcare providers, educators, and social workers for personalized guidance
Remember, there is no single pathway to success, and support is available through multiple channels. If you are uncertain where to start, reach out to your local health department, school district, or child welfare agency for recommendations.
Key Takeaways
In summary, the greatest impact on the lifestyle of young children is exerted by the family environment and socioeconomic status, closely followed by quality education, physical health, and environmental safety. By understanding these factors and leveraging available resources, caregivers and community leaders can create supportive conditions for healthy childhood development.
References
- [1] Jirout, J. (2019). How Lifestyle Factors Affect Cognitive and Executive Function in Children.
- [2] Focus on Kids Pediatrics (2024). Environmental Factors That Affect Child Development.
- [3] Health.gov (2022). Early Childhood Development and Education.
- [4] Marquette University (2023). Factors That Influence Growth and Development.
- [5] National Research Council (2004). Influences on Children’s Health.
MORE FROM gowithdeal.com